Introduction to Underwater and Underground Explosion Phenomena in Abaqus
Abaqus is a robust finite element analysis (FEA) software that simulates complex phenomena, including underwater and underground explosions. These simulations are crucial for defense applications, mining engineering, offshore structures, and protective design
Underwater Explosions in Abaqus
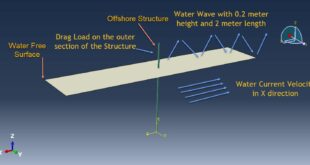
Rapid expansion of gas bubbles creates shock waves
Rapid expansion of gas bubbles creates shock waves
Strong fluid-structure interaction effects
Complex pressure wave propagation through water
Modeling Approaches
Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian (CEL) method: Most common approach where water is modeled as an Eulerian material and structures as Lagrangian
Acoustic medium approach: For far-field effects where nonlinearities are less important
SPH (Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics): For extreme deformation cases
Important Considerations
Equation of state for water (usually Mie-Grüneisen), Shock wave propagation characteristics, Bubble dynamics, and collapse effects, Free surface and boundary reflections
Underground Explosions in Abaqus
Key Characteristics
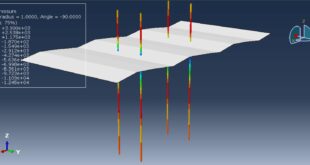
Soil/structure interaction effects
Crater formation and soil ejecta
Stress wave propagation through heterogeneous media
Pore pressure effects in saturated soils
Modeling Approaches
Conventional Lagrangian approach: For small deformation cases
CEL method: For large deformation and soil flow
Porous media models: For saturated soil conditions
Important Considerations
Soil constitutive models (Drucker-Prager, Cap models, etc.), Strain rate effects on soil strength, Pore fluid coupling for saturated soils, Depth and confinement effects on explosion behavior
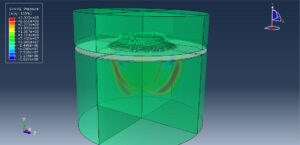
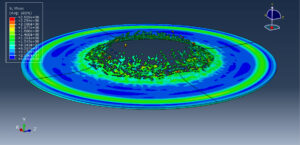
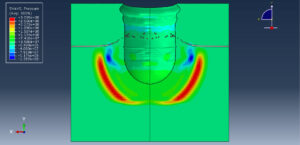
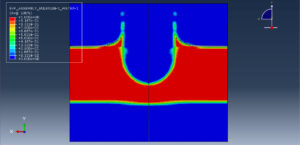
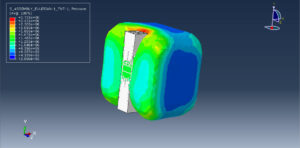
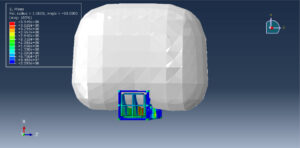
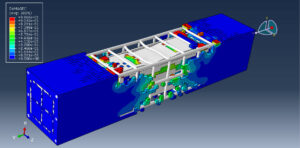
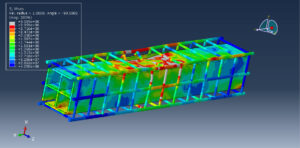
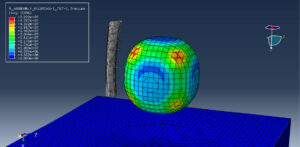
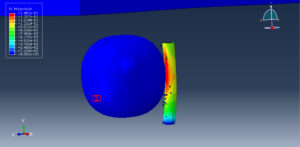
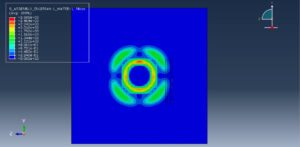
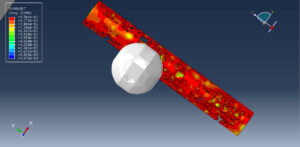
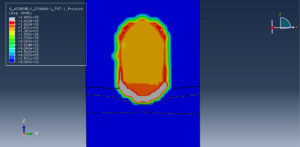
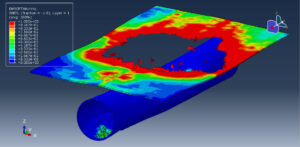
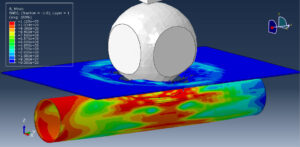
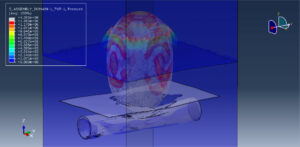

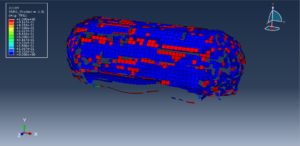
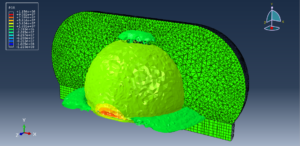
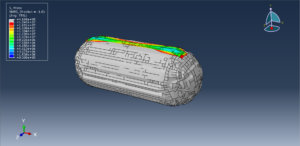
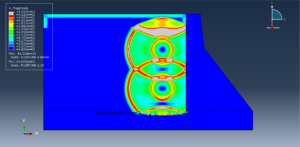
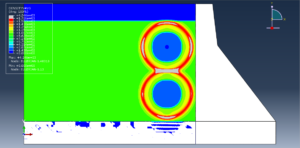
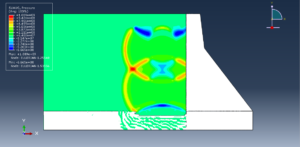
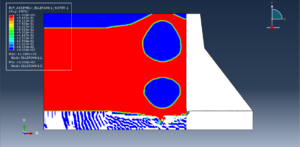
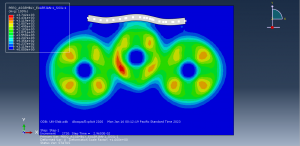
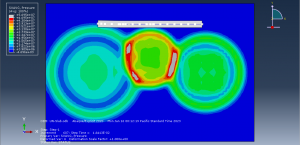
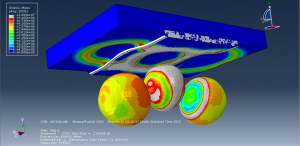
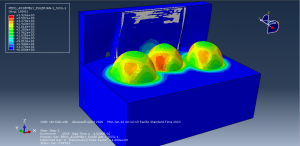
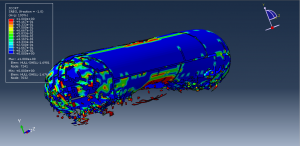
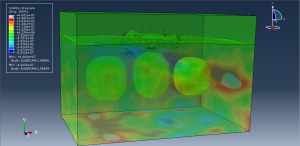
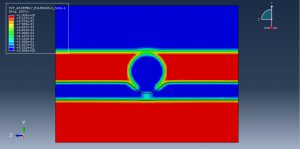
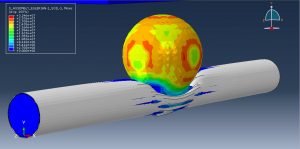
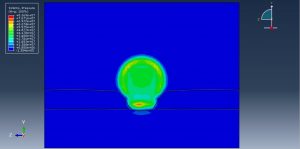
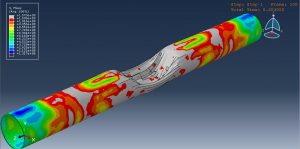
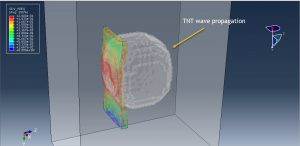
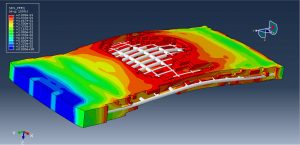
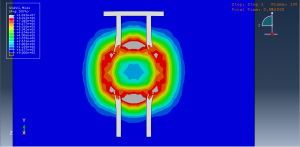
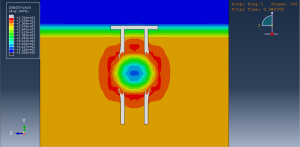
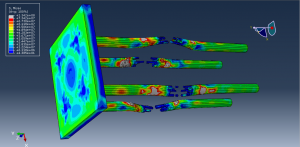
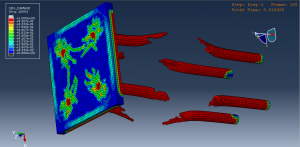
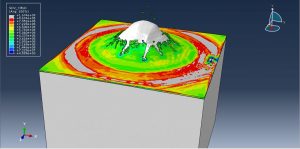
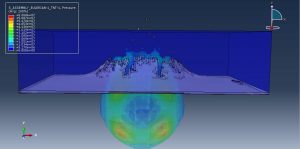
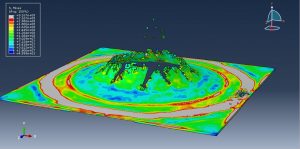
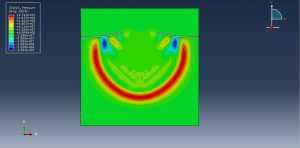
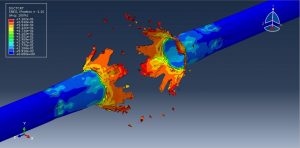
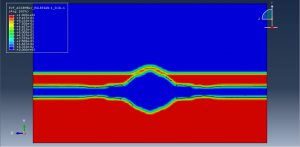
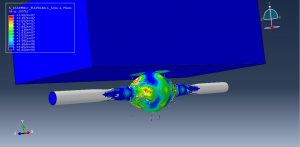
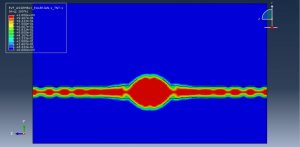
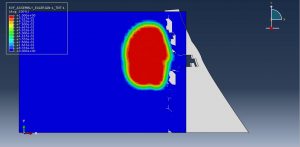
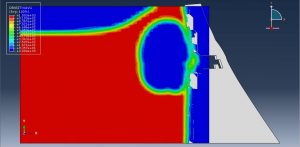
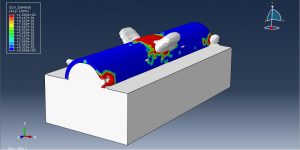
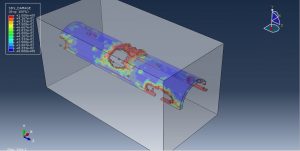
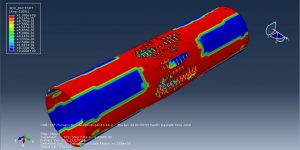
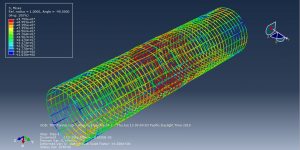
Abaqus provides robust capabilities for these challenging multiphysics problems, though they require careful model setup, appropriate material definitions, and often significant computational resources. The choice of specific modeling approach depends on the problem’s focus (near-field vs far-field effects, structural response vs medium response, etc.)


 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials