The use of aluminum in the construction of automobiles is on the rise in order to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency. This raises an important issue on how to join aluminum parts efficiently and economically and also the need to characterize the mechanical properties of welds. There are many methods
available to join aluminum: tungsten inert gas (TIG), metal arc welding (MIG) and resistance spot welding (RSW) to name a few. All the above methods require heating/melting of the aluminum alloy base metal.Other methods which do not require melting of aluminum alloy base metal are self piercing riveting (SPR), clinching and bonding with structural adhesives to name a few. Spot friction stir welding (SFW) also known as friction stir spot welding (FSSW) is a novel variant of the“linear”friction stir welding (FSW) process developed by Mazda Corporation and Kawasaki Heavy Industries in 2003 as a solid state joining technique to join aluminum alloys. FSW, which was invented by The Welding Institute (TWI) in 1991 and SFW are promising joining processes that have shown potential practical applications for welding aluminum alloys in the automotive industry. FSW and SFW have been successfully used to produce high-quality joints and these methods also make it possible to join high strength aluminum alloys on the basis of tensile strength, process time, and cost (equipment and running cost). Aluminum alloy sheets having a wide range of thickness were joined using the above three methods. It was concluded that the lap-shear strength of joints produced by the SFW process were comparable to those produced by RSW or SPR, however, the process time required to join the sheets using SFW increased monotonically with increasing thickness. SFW process advantages are lower power consumption than RSW, and lower running costs. Furthermore, unlike RSW, no weld spatter occurs during the SFW process, resulting in a better work environment. Other merits of the SFW process include long tool life, high productivity and high reliability.
In this simulation Friction Stir Spot Welding by using Arbitrary Lagrangian- Eulerian method has been investigated. Aluminium alloy is used as base material and toll is modeled as rigid body. Dynamic explicit step by some modification to consider temperature variable has been used. You can see a X-ray figure about the real process at below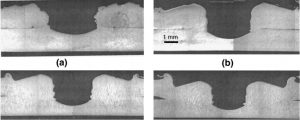
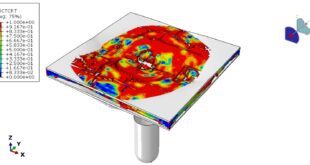
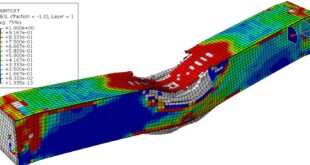
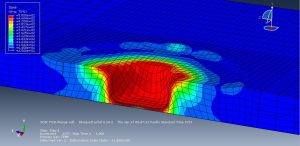
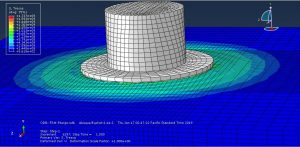
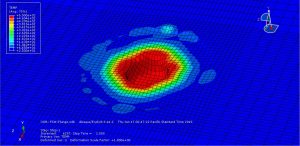
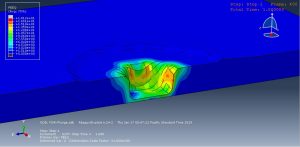
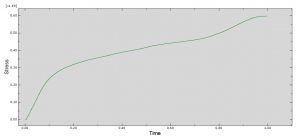
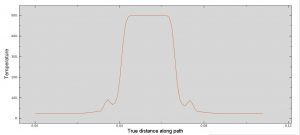
The key point in this simulation is using a proper ALE method to achieve the best result with a regular time. During the analysis the rotational tool with axial velocity penetrated into the aluminium plate and the stress distribution and temperature are obvious .You can see some figures of this simulation at below.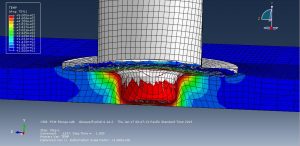

You can provide CAE ,INP,and English video files of this simulation here. The cost of these files is Thirty-Three Euros. you can click on the bellow bottom to beginning process
You can purchase the tutorial through a PayPal account, a Visa, or a Master card, just before payment,send me an email to this address: karampourp@gmail.com
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials