In this tutorial Simulation three dimensional fatigue phenomenon in Abaqus by using Paris law has investigated. Metal fatigue is the process by which a material is slowly damaged by stresses and strains that are less than those needed to actually break the material apart. For example, a steel wire might be used to suspend weights that are less than the amount needed to cause the wire to break apart (its tensile strength). Over time, however, those weights might slowly cause defects to develop in the steel. These defects might occur as scratches, notches, particle formation, or other abnormalities. At some point, these defects may become so great that the steel wire actually breaks apart even though its tensile strength had never been exceeded. The process of metal fatigue varies considerably from one material to another. In some cases, defects show up almost as soon as stresses and strains are applied to the material and grow very slowly until total failure occurs. In other cases, there is no apparent damage in the material until failure almost occurs. Then, in the very last stages, defects appear and develop very rapidly prior to complete failure. The amount of stress or strain needed to bring about metal fatigue in a material—the fatigue limit or fatigue strength of the material—depends on a number of factors. First is the material itself. In general, the fatigue limit of many materials tends to be about one quarter to three quarters of the tensile strength of the material itself. Another factor is the magnitude of the stress or strain exerted on the material. The greater the stress or strain, the sooner metal fatigue is likely to occur. Finally, environmental factors are involved in metal fatigue. A piece of metal submerged in a salt water solution , for example, is likely to exhibit metal fatigue sooner than the same piece of metal tested in air. Similarly, materials that have undergone some oxidation tend to experience metal fatigue sooner than unoxidized materials
In this simulation steel solid part is used with elastic material couple with traction separation law to consider crack growth inside it.Direct cyclic step with maximum one hundred cycle has used.
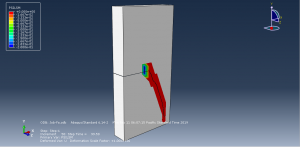
To define fatigue behavior Paris law as input file with Power law to consider the fracture parameter is used. during the process the crack growth and fatigue data are achievable in visualization for each cycle.You can see some figures of the simulation results at below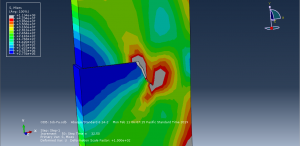
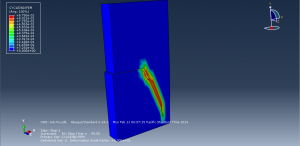
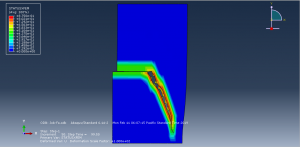
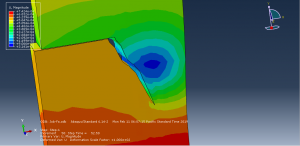
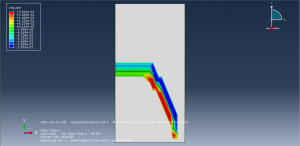
You can provide CAE ,INP,and English video files of this simulation here. The cost of these files is Twenty-Six Euros. you can click on the bellow bottom to beginning process
You can purchase the tutorial through a PayPal account, a Visa, or a Master card, just before payment,send me an email to this address: karampourp@gmail.com
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials