In this tutorial Simulation, Sequential Construction of an Embankment on a Clay Layer in Abaqus has been investigated. The two-dimensional part is used for modeling the clay layer and three layers of the embankment. You can see a figure of the assembling part ate below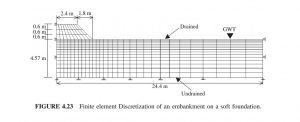
Each embankment layer is constructed in a two-day period, during which consolidation of the clay layer takes place. The total construction time is six days. Assume that the embankment material is a linear elastic material. The clay layer is assumed as a Porous elastic with cam-clay plasticity. For both materials, permeability is used. Initially, the clay layer is constructed in one calculation step (step 1) and its effective self-weight is applied using the “body-force” option. The top surface of the clay layer is assumed to be permeable. The clay layer is assumed to be elastoplastic, obeying the modified Cam clay model. Using such a model is essential for this class of analysis because we are concerned with the ability of the clay layer to withstand the stresses caused by the sequential construction of the embankment. A model like this one can detect the failure within the clay layer during and after construction. During step 1, a “geostatic” command is invoked to make sure that equilibrium is satisfied within the clay layer. The geostatic option makes sure that the initial stress condition in any element within the clay layer falls within the initial yield surface of the Cam clay model. Next, the first embankment layer is constructed on top of the clay layer in a separate calculation step (step 2). The self-weight of the first embankment layer is gradually applied, using the “body-force” option, in a two-day period. Now, it is important to change the hydraulic boundary condition at the interface between the clay layer and the first embankment layer. As you recall, in step 1 the top surface of the clay layer was assumed to be permeable. In the present step 2, we will need to make the permeable boundary condition inactive only at the interface between the clay layer and the first embankment layer. If we don’t, the old boundary condition will act as a drain between the clay layer and the embankment. Further, we need to apply a permeable boundary condition on top of the first embankment layer and also on its sloping face. This will allow the excess pore pressure to drain during the two-day period. Note that the embankment soil is assumed to be more permeable than the underlying clay layer. In step 3 we construct the second embankment layer in the manner described above. Again, we will need to make the permeable boundary condition at the interface between the first and second embankment layers inactive. Also, we need to apply a permeable boundary condition on top of the second embankment layer and on its sloping face. In step 4 we construct the third (last) embankment layer following the exact procedure for layer 2. Step 5 is a consolidation step with a duration of 200 days
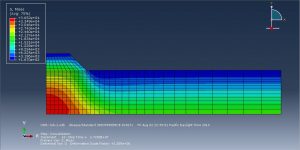
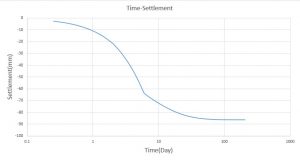
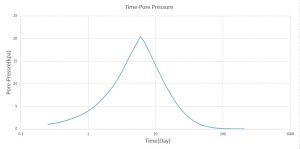
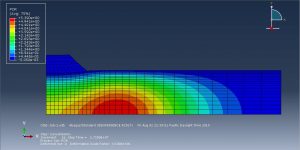
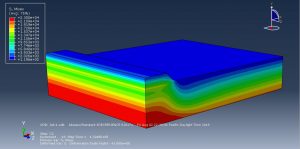
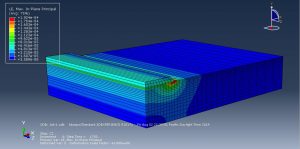
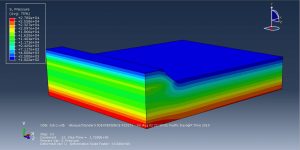
The goal of this simulation to figure out the settlement-time and pore pressure-time diagram which they drew after the simulation. You can see figures of the result at below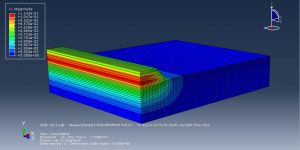
You can provide CAE ,INP,and English video files of this simulation here. The cost of these files is Twenty-Three Euros. you can click on the bellow bottom to beginning process
You can purchase the tutorial through a PayPal account, a Visa, or a Master card, just before payment,send me an email to this address: karampourp@gmail.com
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials