In this tutorial, the Simulation of the Kalthoff–Winkler experiment crack growth using a XFEM peridynamic model under low-velocity impact in Abaqus has been investigated. Both two- and three-dimensional models can be used to model the plate. The example implanted based on the Abaqus manual for Kalthoff-Winkler test
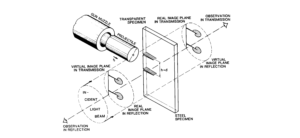
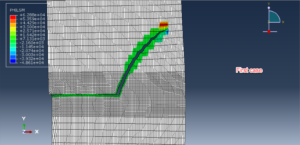
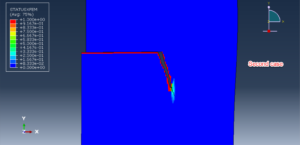
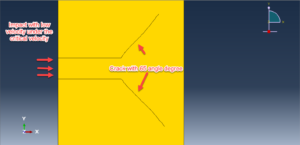
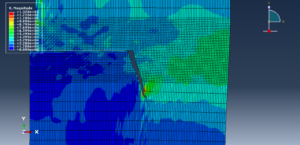
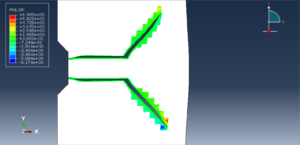
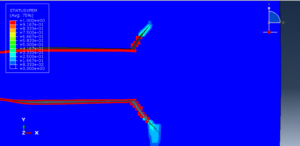
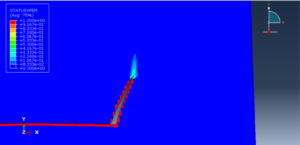
Fracture and failure analysis has always been one of the major concerns in theoretical studies and engineering applications. For mode II dynamic loading conditions with high rates, experiments have demonstrated that failure in shear form can be easily obtained if suitable fixtures are applied. The technique of loading edge cracks by edge impact (LECEI) introduced by Kalthoff provides such a fixture, in which a loosely positioned flat plate (target) with two parallel notches is impacted by a projectile. During the impact process, a compressive stress wave is triggered, and the displacement associated with this stress wave creates a pure shear mode II loading condition in a very short time period, and an effective mode II crack propagation path can then be observed. The Kalthoff-Winkler experiment is a benchmark dynamic fracture problem for predicting crack propagation in an impact-loaded pre-notched plate.
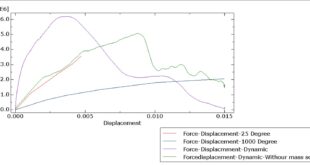
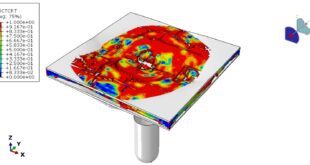
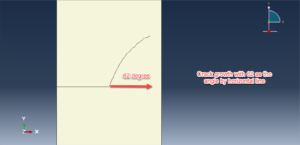
In this tutorial, three cases are investigated. The crack angle in all three cases is matched with the experiment. The Abaqus manual used XFEM method for this test under low-velocity impact. You can see some figures of the results below
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials