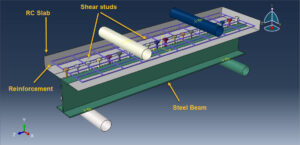
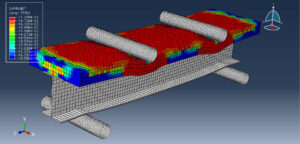
In this tutorial, the Simulation of shear stud distribution on load capacity of the steel-concrete composite beam in Abaqus has been investigated. The concrete slab, steel beam, and studs are modeled as three-dimensional solid parts. The steel reinforcements are modeled as wire parts. You can see a figure of the assembled parts below
Recently, there has been a wide use of steel–concrete composite beams in buildings and bridge construction. Their advantages include high bending capacity and stiffness due to the benefits of composite action and high speed of fabrication and construction. Despite an improved understanding of their behavior, several composite structures failed to satisfy their structural and functional demands due to stud shearing of concrete crushing as a direct result of fatigue
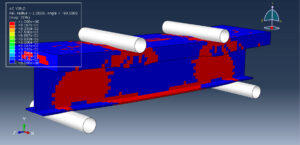
The Concrete Damaged Plasticity model is selected to model concrete material under bending load. The model is a continuum, plasticity-based, damage model for concrete. It assumes that the main two failure mechanisms are tensile cracking and compressive crushing of the concrete material. The elastic-plastic model is selected for all the steel members like steel beams, studs, and reinforcements
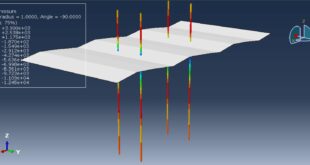
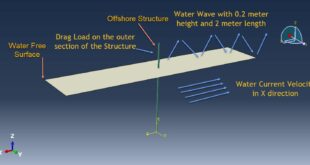
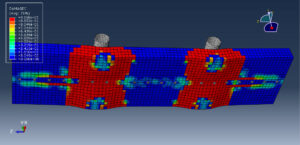
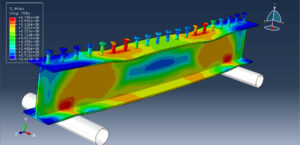
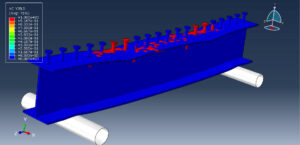
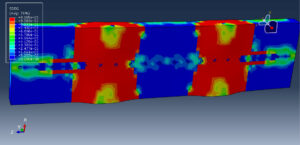
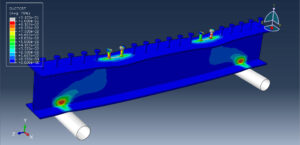
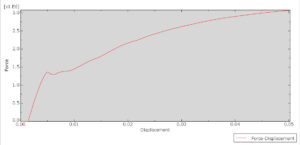
The general static step is appropriate for this analysis, in the interaction, all contacts and constraints are assigned to all parts. The proper mesh and boundaries are applied to all parts. After the simulation, all results such as stress, strain, tension damage, compression damage, force-displacement diagram, and others are available. You can see some figures of the results below
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials