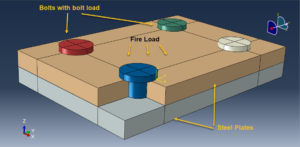
In this tutorial, the Simulation fire analysis of a steel joint with bolt connectors in Abaqus has been investigated. The two steel plates are modeled as three-dimensional solid parts. The bolts are modeled as three-dimensional parts. You can see a figure of the assembled parts below
Steel has been at the forefront of efficient construction in the last few years, where it has been used widely in the construction of high-rise buildings, industrial structures, and residential structures. What makes steel one of the most appealing materials in the construction industry is its engineering properties. The most appealing properties of steel are its strength-to-weight ratio, ductility, and flexibility. Such properties allow designers to build structures such as skyscrapers, which certainly would have not been possible with any other material. Steel can also be prefabricated and shipped to construction sites easily, which is quite beneficial when it comes to meeting the ever-increasing demands of new buildings. Nevertheless, there is a huge downside to using steel as a construction material because of its low resistance to fire when compared to other construction materials such as concrete. Steel loses almost half of its strength when subjected to temperatures that are equal to or greater than 590 °C, which will eventually lead the structure to fail. The losses that follow structural failures caused by fire are colossal and can take different forms, such as loss of human lives, environmental loss, and economic loss. Hence, the insurance of structural stability of a building under fire loading has been one of the most important and challenging aspects when it comes to designing a new structure. It is important that in the event of a fire, structures can withstand the minimum level of life safety not only for the occupants but also for firefighters and the public that are in proximity to the building. The minimum level of fire safety design must ensure a reduction of the risk of deaths and injuries, protect the contents of a building, and ensure that the building continues to function after the fire with the least amount
The elastic-plastic material data depends on the temperature selected for both heat transfer and static analysis. First, the heat transfer model uses conduction and convection as the fire load is applied and the nodal temperatures are extracted. In the second model, the static analysis with bolt load as the pre-load is applied to the bolts, and the fire results from the previous model are considered as the initial state of the model.
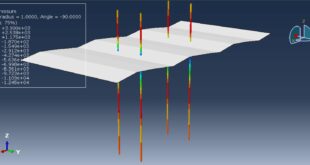
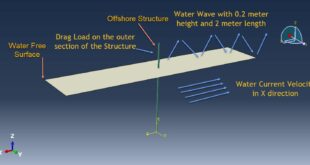
In both models, the proper boundary and mesh are used. After the simulation, all results such as temperature, degradation, stress, strain, displacement, and others are available. You can see some figures for the results below
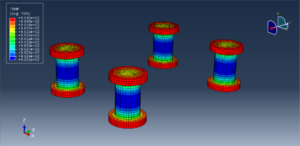
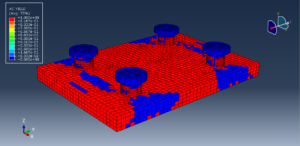
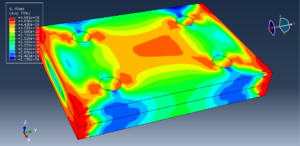
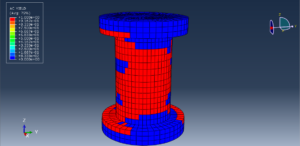
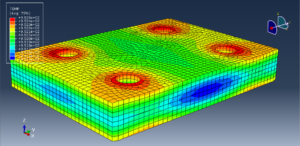
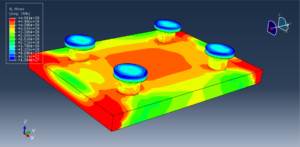
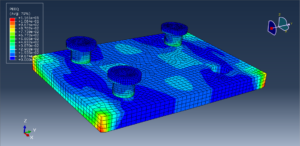
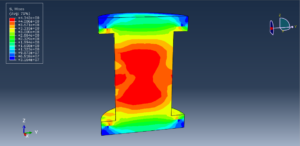
You can provide CAE, INP, and English video files of this simulation here. The cost of these files is Thirty Euros. you can click on the bellow bottom to begin the process
You can purchase the tutorial through a PayPal account, a Visa, or a Master card, just before payment, send me an email to this address: karampourp@gmail.com
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials