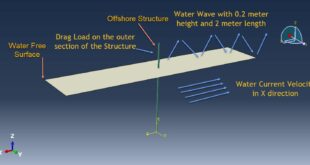
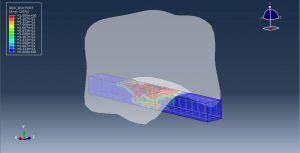
In this tutorial, the Simulation Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian Explosion over the Reinforced Concrete Beam in Abaqus has been investigated. Blast incidents in recent years showed that most of the terrorist attacks on public structures were explosions within short standoff distance. Reinforced concrete (RC) structures are widely used in civil engineering for many reasons such as price, weathering and fire resistance but RC members have been proved to be vulnerable under explosions. In this context, columns are the most vulnerable structural components and their failure is the primary cause of the progressive collapse in framed structures. n the other hand, many of the research efforts in this field have been devoted to the effects of far-field explosions on structural elements. The effects of near-field explosions on structural elements. The three-dimensional model is used in this simulation. You can see figures of the assembled parts below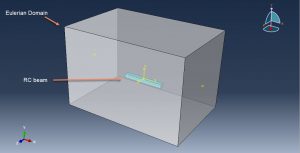
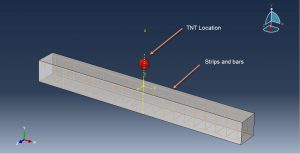
The Jones-Wilkens-Lee (or JWL) equation of state models the pressure generated by the release of chemical energy in an explosive. This model is implemented in a form referred to as a programmed burn, which means that the reaction and initiation of the explosive are not determined by shock in the material. Instead, the initiation time is determined by a geometric construction using the detonation wave speed and the distance of the material point from the detonation points. The parameters for the JWL model for the TNT are extracted from the reference paper. To model bars and strips, steel material with elastic-plastic(JC) behavior is used. To model concrete behavior under massive and huge pressure load, the Johnson-Holmquist material model is appropriate. The JH-2 model assumes that the damage variable increases progressively with plastic deformation. The dynamic explicit step is proper for this type of simulation. The general contact with contact property is implied to consider all contacts in the Eulerian domain. The bars and strips are embedded inside the concrete host. The fixed boundary condition is assigned to the two ends of the beam and zero velocity to the bottom surfaces of the domain. The volume fraction method is used to specify the amount and location of the TNT part inside the concrete domain. The mesh should be fine to achieve good results
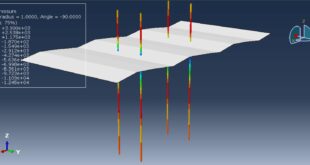
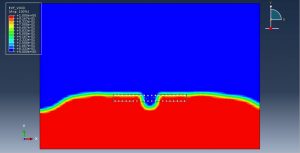
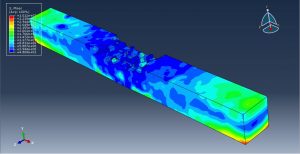
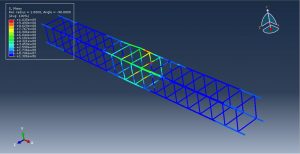
After the simulation, all results such as damage variable, plastic strain, failure, TNT wave propagation, … are achievable. You can see some figures for the results below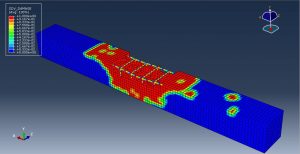
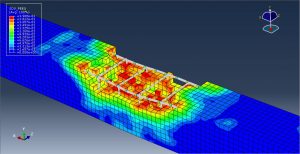
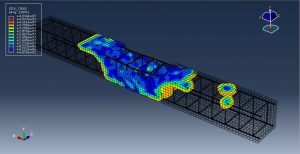

You can provide CAE ,INP,and English video files of this simulation here. The cost of these files is Twenty-Seven Euros. you can click on the bellow bottom to beginning process
You can purchase the tutorial through a PayPal account, a Visa, or a Master card, just before payment,send me an email to this address: karampourp@gmail.com
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials