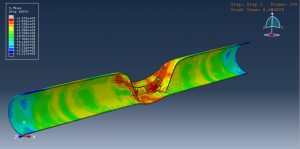
In this tutorial, the Simulation CEL explosion in the depth of soil near a solid steel pipe in Abaqus has been done. The Eulerian domain is modeled as a three-dimensional Eulerial part. The air, soil, and TNT are modeled as three-dimensional solid part. The steel pipe is model as a three-dimensional solid part. You can see a figure of the assembled parts below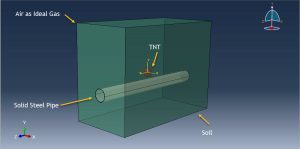
Used for distribution of water, gas, oil, etc., buried pipelines are considered among the most important elements of lifelines. Buried pressurized gas pipelines are bound to be threatened by accidental explosions in process industries, explosives factories, open pit mines, quarries, public works or even intentional explosions near a pipeline. Terrorist attacks have unfortunately been increasing so that multiple explosions, in recent years, have taken place in the route of oil and gas transmission pipelines. Accordingly, blast loads and the design and the analysis of buried structures under destructive dynamic loads are particularly attended in recent years. To model steel pipe behavior under severe load elastic-plastic material data is selected. The Johnson-Cook plasticity with Johnson-Cook damage to consider steel pipe failure during the detonation is used. To model air material, ideal gas equation of state with dynamic viscosity is considered. To model soil behavior, elastic data with Mohr-Coulomb plasticity is used. The Jones-Wilkens-Lee (or JWL) equation of state models the pressure generated by the release of chemical energy in an explosive. This model is implemented in a form referred to as a programmed burn, which means that the reaction and initiation of the explosive is not determined by shock in the material. Instead, the initiation time is determined by a geometric construction using the detonation wave speed and the distance of the material point from the detonation points The dynamic explicit step is appropriate for this type of analysis. The general contact capability with contact property is used. The non reflecting boundary is assigned to the outer surfaces of the Eulerian domain. The fixed boundary condition is assigned to the two ends of the pipe. The volume fraction method is used to define the location of the each materials in the Eulerian domain. The mesh should be fine to obtain better results
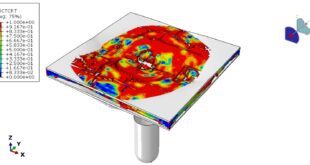
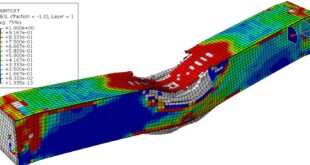
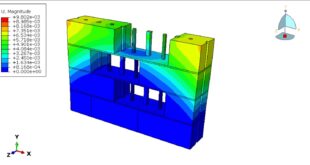
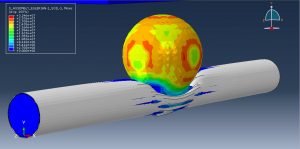
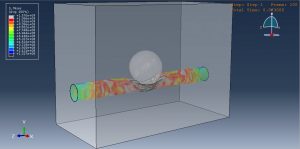
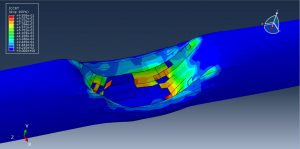
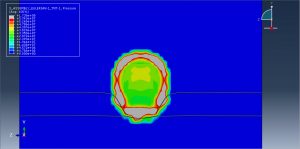
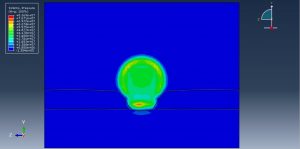
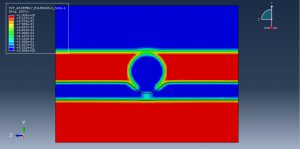
After the simulation, all results such as stress, strain, damage, failure, detonation wave propagation, volume fraction, and … are available. You can some figures for the results below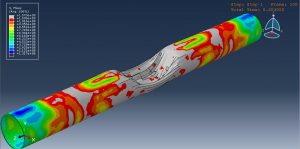
You can provide CAE ,INP,and English video files of this simulation here. The cost of these files is Twenty-Eight Euros. you can click on the bellow bottom to beginning process
You can purchase the tutorial through a PayPal account, a Visa, or a Master card, just before payment,send me an email to this address: karampourp@gmail.com
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials