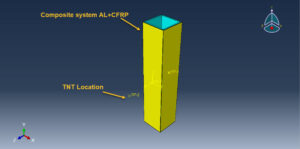
Simulation air blast explosion over an aluminum box reinforced with CFRP layers in Abaqus has been studied in this tutorial. The aluminum box is modeled as a three-dimensional solid part. The CFRP layers are modeled as four separated part with different orientations. You can see figures of the assembled parts below

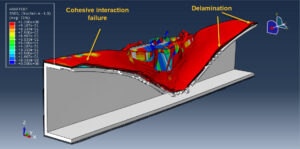
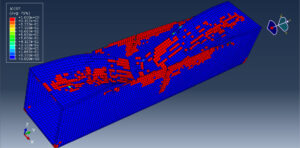
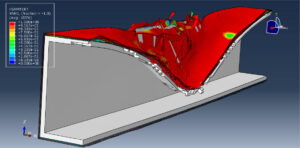
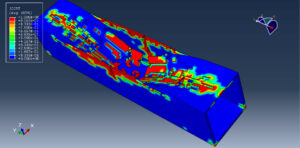
The Johnson-Cook model is a plasticity model that is based on Mises plasticity with closed-form analytical equations specifying the hardening behavior and the strain-rate dependence of the yield stress. The Johnson-Cook criterion is a special ductile damage initiation criterion in which the equivalent plastic strain at the onset of damage is given as an analytical function of stress triaxiality. The JC hardening and damage are used to define aluminum material behavior under severe load and high rate deformation. The Hashin criterion identifies four different modes of failure for the composite material. The four modes are tensile fiber failure, compressive fiber failure, tensile matrix failure, and compressive matrix failure. To model CFRP behavior and its damage, the Hashin damage model is selected.
The dynamic explicit step is appropriate for this type of analysis. The cohesive contact is assumed between aluminum and CFRP, and CFRP to CFRP interaction. The CONWEP air blast load is considered the detonation method. The proper boundary conditions and meshes are assigned to all parts
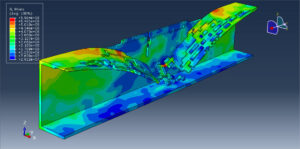
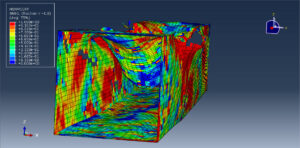
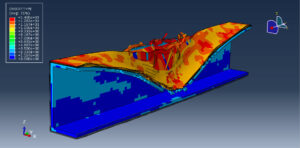
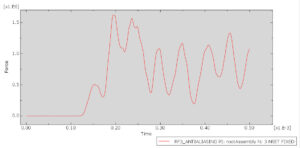
After the simulation, all results such as stress, strain, aluminum damage, CFRP fiber and matrix damage, element deletion, and others are available. You can see some figures for the results below
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials