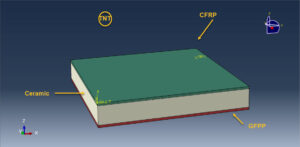
Simulation air blast explosion over a composite panel(CFRP-Ceramic-GFPP) in Abaqus has been investigated in this tutorial. The CFRP and Glass fiber Polypropylene are modeled as shell parts with some layers. The ceramic core is modeled as a solid part. You can see a figure of the assembled parts below
The JHB model consists of three main components: a representation of the deviatoric strength of the intact and fractured material in the form of a pressure-dependent yield surface, a damage model that transitions the material from the intact state to a fractured state, and an equation of state (EOS) for the pressure-density relation that can include dilation (or bulking) effects as well as a phase change. To model ceramic under the severe pressure load, the JHB material is selected
The Hashin criterion can be implemented in conjunction with a damage evolution law, which is based on the specification of four fracture energy Gf values, each corresponding to the material degradation in each mode. The Hashin criterion identifies four different modes of failure for the composite material. The four modes are tensile fiber failure, compressive fiber failure, tensile matrix failure, and compressive matrix failure. To model CFRP and GFPP composite material, the Hahsin damage criterion is considered
Dynamic explicit steps with perfect contact among the parts are used. The CONWEP air blast method by using the mass of TNT and its locations is a good selection to define the explosion phenomenon. Proper boundary conditions and meshes are assigned to all parts
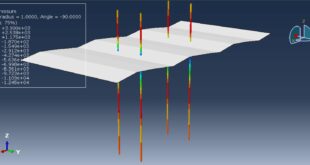
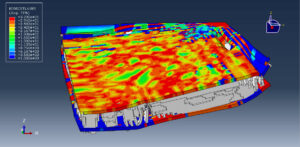
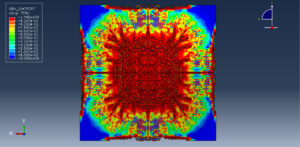
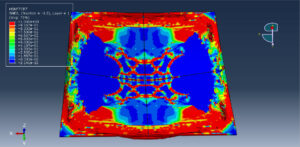
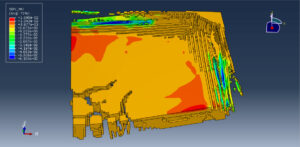
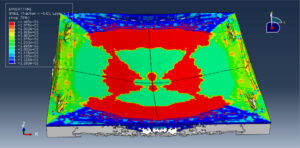
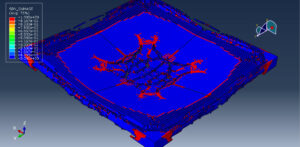
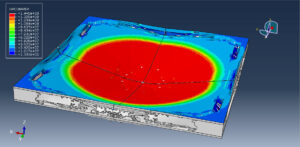
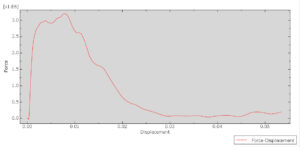
After ending the analysis, all results such as stress, strain, damage of composite layers, ceramic failure, and others are available. you can see some figures of the results below
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials