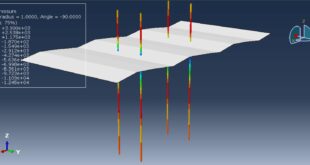
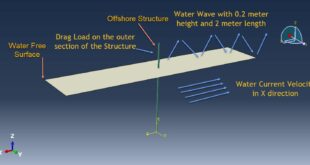
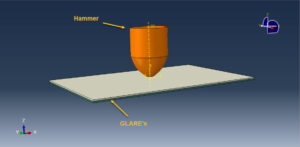
The numerical simulation on the high-low velocity impact response of GLAREs in Abaqus software has been investigated. The model contains metal aluminum layers and glass fiber. You can see a figure of the assembled parts below
In recent decades, the demand for high‐performance materials has increased significantly in various sectors of the aviation and automobile industries. FMLs are a suitable alternative to conventional aluminum sheets that combine the high bearing strength, impact resistance, and isotropic nature of aluminum with high strength, low density, and good fatigue performance of composites. The low-velocity impact incidents, such as falling tools, runway debris, gravel, and hail may lead to internal damage to the specimen during the maintenance, manufacturing, and flight processes
Glassfiber aluminum laminates (GLAREs) are a type of fiber metal laminates (FMLs) that are widely used in the aviation industry. performed the three-D numerical analysis of the high-low velocity impact on sandwich panels with FML face sheets and examined the impact of fiber materials, face sheet metals, and impact energy on the response of structures. The results showed that changing the fibers from glass to carbon and boron and changing the metal from aluminum to titanium and manganese increase the energy absorbed by the structure. Delamination is a critical damage mode in impacted FMLs. For this reason, the finite element models proposed to simulate FMLs under impact must be able to calculate delamination on a ply-by-ply base
Dynamic explicit solver is selected to consider low-high velocity impact on the GLAREs. The cohesive interaction is used between the metal and composite layers. Proper boundaries and mesh are assigned to all parts
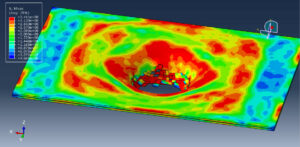
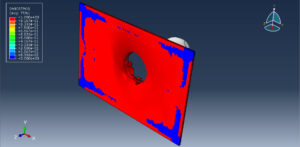
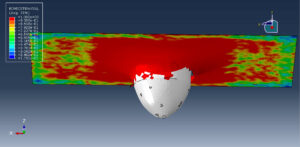
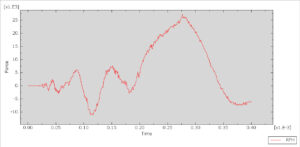
After the simulation, all results such as stress, strain, damage, failure, force, and others are available. You can see some figures for the results below
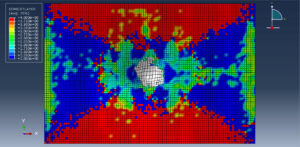
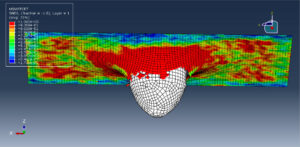
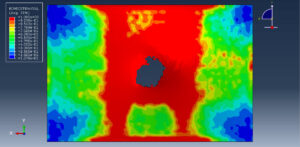
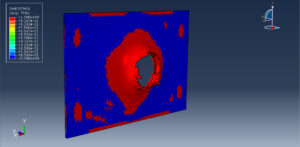
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials