The erection of a water wall around an explosive has been found to be an effective method of mitigating the effect of shock wave and blast pressure of an accidental explosion. Essentially, the high-pressure shock wave produced by detonation aerosolizes the water placed close to explosive and causes both a phase change of water and the re-distribution of internal and kinetic energy over the detonation gases, the blast wave and barrier material. In view of its effectiveness in attenuating explosions, the water mitigation concept begins to attract much attention in both defense and commercial applications for the storage of energetic materials.An explosion is a phenomenon resulting from a sudden release of energy. Usually, after detonation the solid explosive is transformed into gaseous products, which initially are at extremely high pressure, which may exceed hundred thousand atmospheres. This pressure is transformed into mechanical work by momentum transfer in the form of pres-sure waves, which propagate into the surrounding medium. Here, the pressure–volume–energy behavior of the detonation product gases of TNT is modeled with the standard Jones–Wilkins–Lee (JWL) equation of state and a detonation velocity of 6,930 m/s.You can see a figure of the experiment test

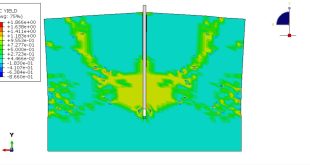
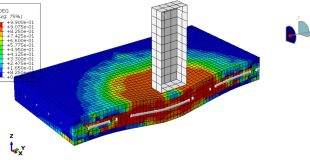
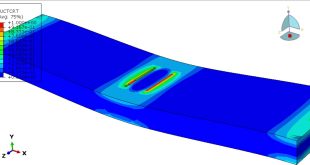
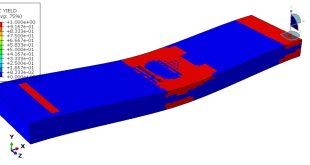
In this simulation all parts are considered as three dimensional Eulerian part. To model water EOS material model as Us-Up equation and for TNT JWL material model were used. Dynamic explicit procedure is appropriate for this type of analysis. You can see some figures of the results of this simulation at below
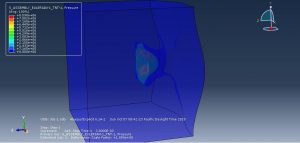
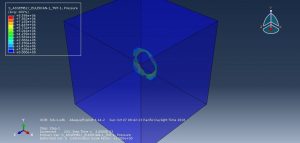
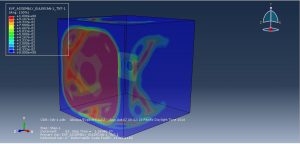
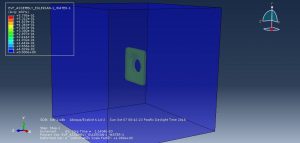
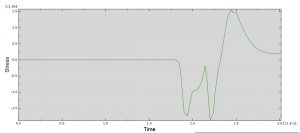
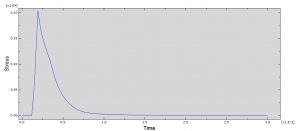
You can provide CAE ,INP,and English video files of this simulation here. The cost of these files is Twenty-Six Euros. you can click on the bellow bottom to beginning process
You can purchase the tutorial through a PayPal account, a Visa, or a Master card, just before payment,send me an email to this address: karampourp@gmail.com
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials