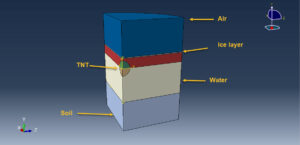
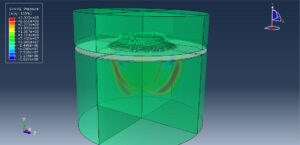
In this tutorial, the Numerical investigation on damage characteristics of ice sheet subjected to underwater explosion load in Abaqus has been studied. The ice is modeled as a three-dimensional solid part. The air, soil, water, and TNT are modeled as an Eulerian part. You can see a figure of the assembled parts below
The ice jam is a common phenomenon in the cold region, and is easy to form, especially in rivers, lakes, and oceans above dimension 30 degrees during periods of freezing and thawing. However, ice jams can seriously threaten human life and property. Hence, more and more effective means to prevent Ice jams are essential. Some experts point out that underwater blast for breaking the ice is a significant approach to eliminating ice jams. At present, an underwater explosion for ice-breaking is a complex fluid-structure interaction issue, and the mechanism of interaction between fluid and ice has not been revealed completely. To analyze this problem, the primary method is included as: (1) theoretical analysis method: a theoretical model is proposed usually based on appropriate assumed conditions, which applies to the simple situation after idealizing shock wave load, but for a complex problem; (2) experimental method: conducting an experimental test need proper parameters conditions to obtain the breaking ice law but incurs massive costs; (3) numerical method: by introducing the appropriate material model and failure criterion, the computer technology can be utilized to study the dynamic of ice and the mechanisms of fluid-ice, such as finite element method
The underwater explosion is a complicated fluid-solid coupling process involving medium flow, large deformation of the structure, nonlinear failure, and so on. With the development of the numerical method, many scholars have improved numerical methods to improve calculation efficiency, such as modified numerical Lagrangian methods, Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE) methods, Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian (CEL) method, Boundary Element Method (BEM), Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH), and so on. Each approach has unique strengths and weaknesses. Because of the advantages of high calculation efficiency and dealing with complicated models, both the ALE method and the CEL method have been successfully integrated into commercial software code, which is widely used in solving all kinds of practical engineering problems, especially underwater explosion problems. Although the Coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian (CEL) method is a typical method that fluid motions are described by traditional Eulerian description where the structure is defined by conventional Lagrangian description, no abundant material model is provided for references about ice material in ABAQUS/Explicit
Dynamic explicit step with general contact capability is a good procedure to perform this analysis. The proper boundary conditions and meshes are assigned to all parts
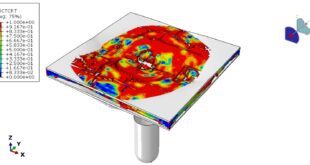
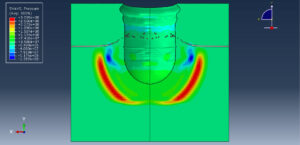
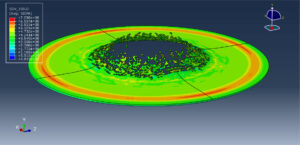
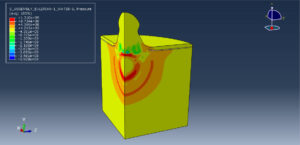
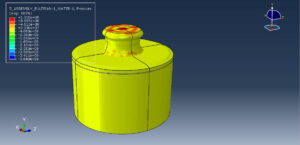
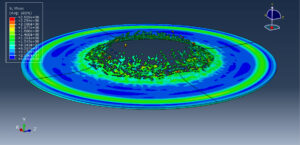
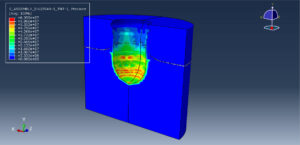
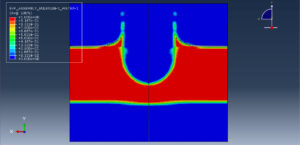
After the simulation, all results such as stress, strain, ice breaking, water wave, TNT pressure, air expansion, and others are available. You can see some figures of the results below
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials