Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) and CFD Analysis in Abaqus
Introduction to Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI)
Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) is a multiphysics phenomenon where a fluid and a solid structure interact, leading to deformation in the structure and changes in the fluid flow. FSI problems are common in engineering applications such as
Aerodynamics (aircraft wings, wind turbines)
Biomedical engineering (blood flow in arteries, heart valves)
Civil engineering (bridge flutter, offshore structures)
Automotive engineering (car aerodynamics, fuel tanks)
Types of FSI Problems
One-way FSI: Fluid forces affect the structure, but structural deformations do not influence the fluid flow (e.g., static pressure loads)
Two-way FSI: Fluid and structure mutually influence each other (e.g., flutter, sloshing, flexible pipes)
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) in Abaqus
Abaqus is primarily a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) software, but can perform CFD simulations using
Abaqus/CFD (standalone module for fluid flow)
Co-simulation with Abaqus/Standard or Abaqus/Explicit (for coupled FSI problems)
Key Features of Abaqus/CFD
Solves Navier-Stokes equations for incompressible/weakly compressible flows, Supports laminar and turbulent flows (k-ε, k-ω models), Mesh motion techniques (ALE – Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian), Coupling with structural solvers for FSI
Coupling Methods in Abaqus
Co-Simulation (Two-way FSI)
Abaqus/CFD (fluid solver) + Abaqus/Standard or Explicit (structural solver)
Data exchange at each time step (pressure/forces → structure, displacements → fluid mesh)
One-way Coupling
Export CFD pressure loads and apply them as static loads in a structural analysis
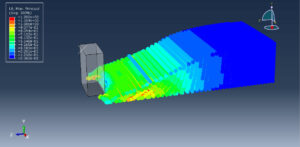
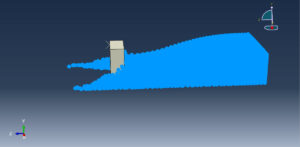
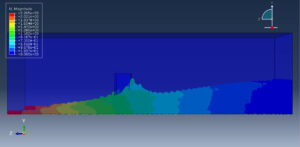
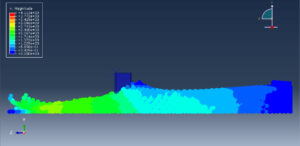
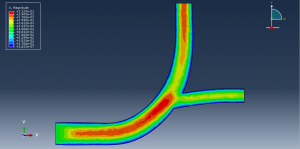
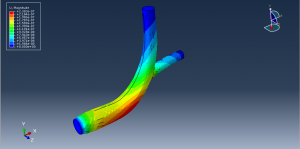
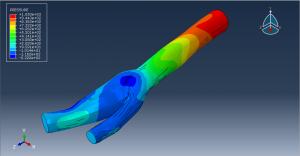
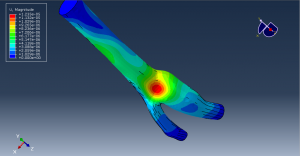
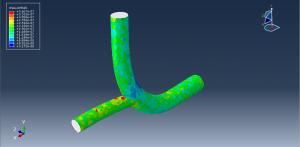
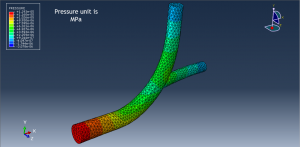
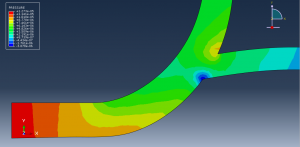
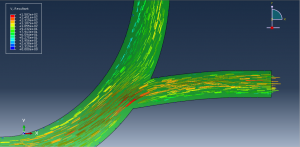
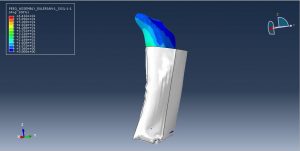
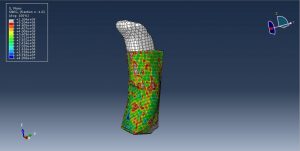
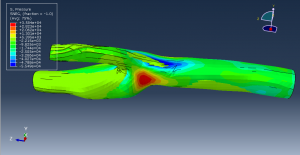
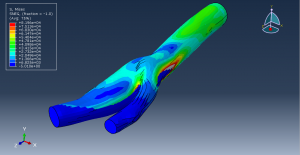
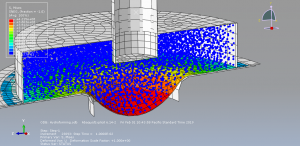
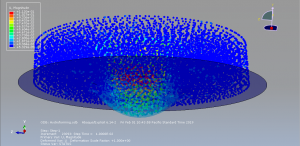
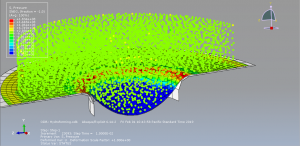
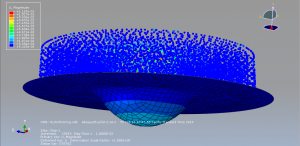
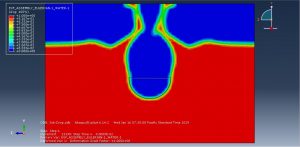
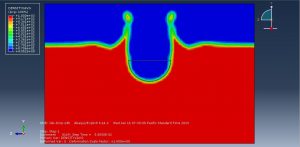
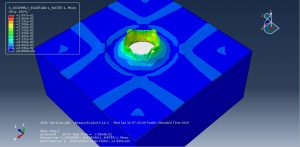
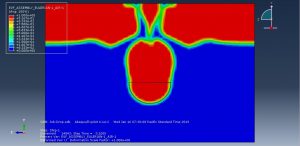
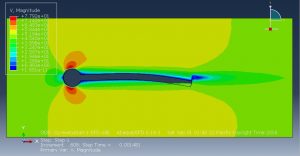
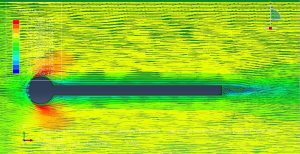
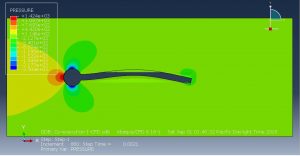
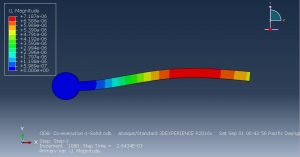
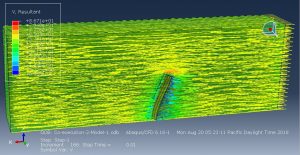
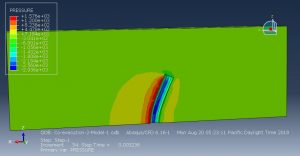

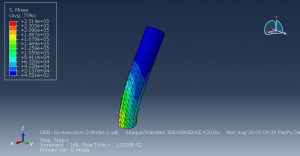
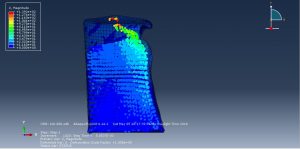
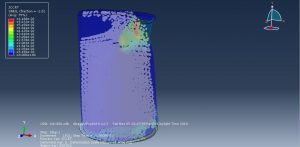
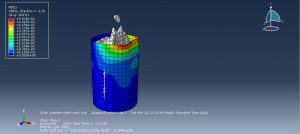
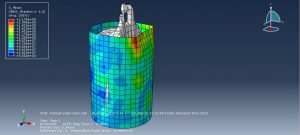
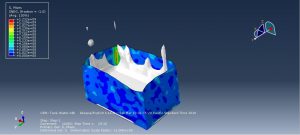
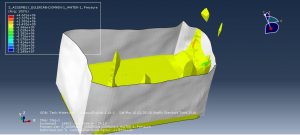
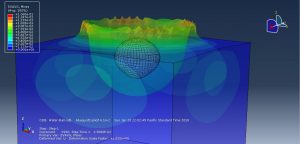
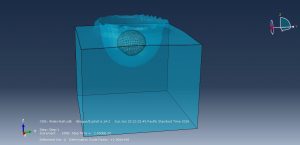
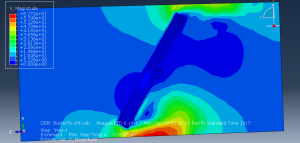
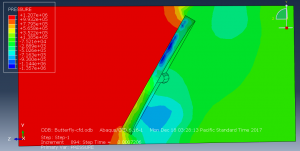
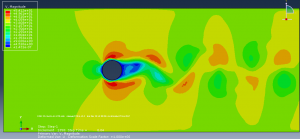
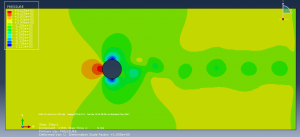
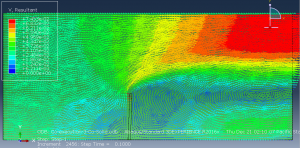
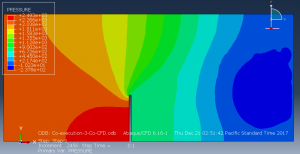
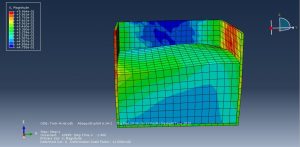
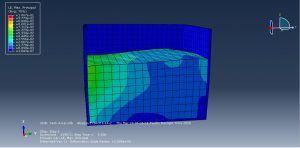
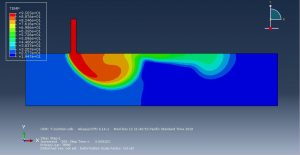
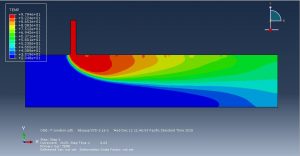
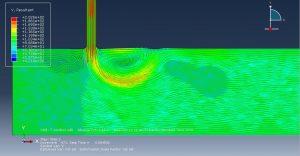
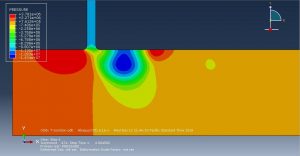
Challenges in FSI Simulations
Mesh Compatibility: Fluid and structure meshes must align at the interface
Numerical Instability: Large deformations may require remeshing or ALE techniques
Computational Cost: High-resolution CFD + structural coupling increases solve time
Convergence Issues: Strong coupling requires sub-iterations for stability
Best Practices for FSI in Abaqus
Start with simplified models before full-scale simulations
Use coarse meshes initially for debugging
Validate with analytical solutions or experiments
Monitor energy balance to ensure stability
Consider parallel computing for faster solutions

Conclusion
FSI is a critical multiphysics problem requiring coupled CFD and structural analysis
Abaqus provides tools for co-simulation and one-way coupling
Challenges include mesh handling, convergence, and computational cost
Proper modeling techniques can simulate real-world FSI problems effectively
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials