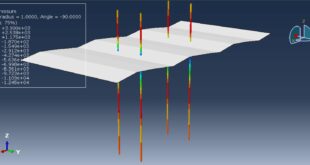
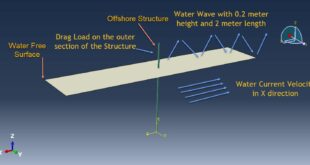
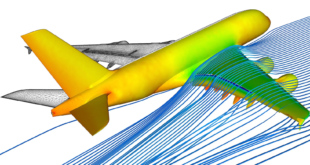
Introduction to Bolt Analysis in Abaqus
Abaqus is a powerful finite element analysis (FEA) software widely used for simulating complex mechanical systems, including bolted joints. Bolt analysis in Abaqus involves modeling the bolt, applying preload, and simulating the behavior of the bolted joint under various loading conditions. This analysis helps engineers understand stress distribution, deformation, and potential failure modes in bolted connections, ensuring the safety and reliability of mechanical assemblies. Bolts are critical components in mechanical assemblies, providing the necessary clamping force to hold parts together. Simulating bolts using the Finite Element Method (FEM) is essential for understanding their behavior under various loading conditions, such as tension, shear, and combined loads. FEM allows engineers to predict stress distribution, deformation, and potential failure points in bolted joints, ensuring the safety and reliability of the assembly
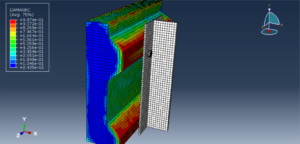
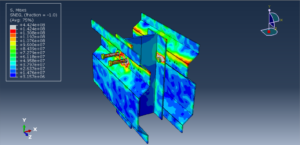
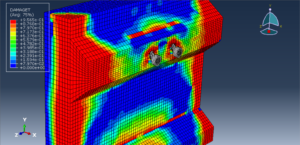
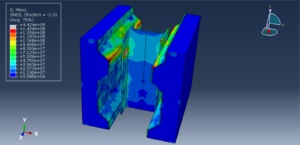
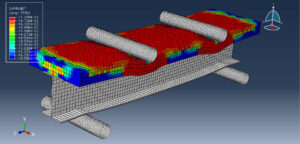
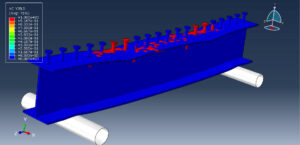
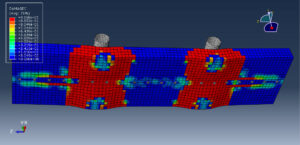
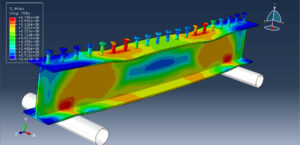
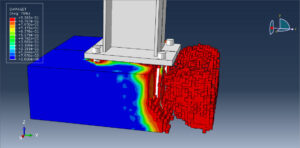
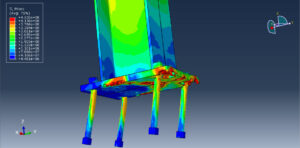
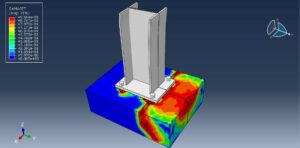
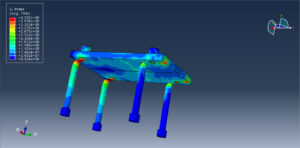
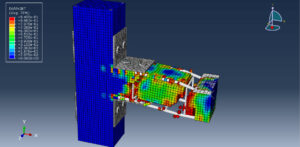
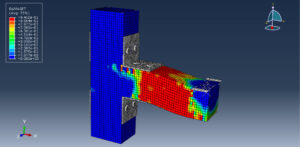
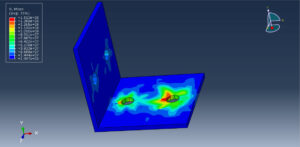
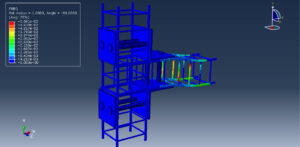
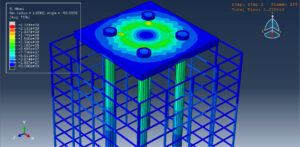
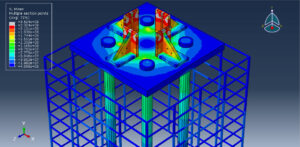
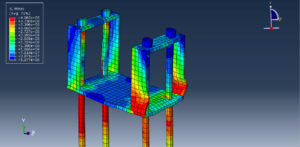
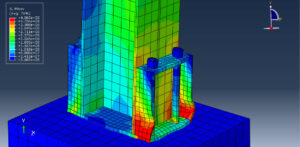
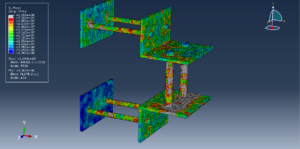
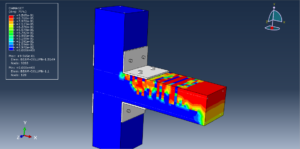
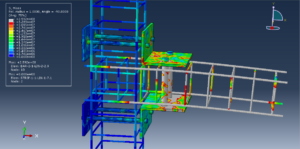
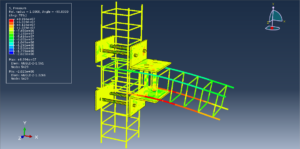
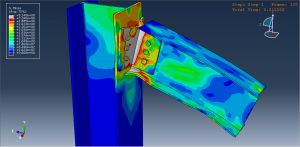
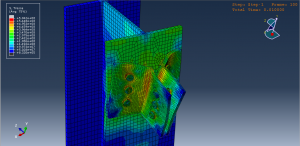
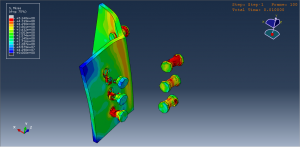
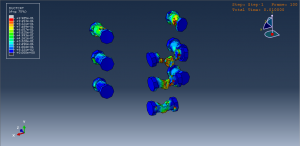
Key Aspects of Bolt Simulation Using FEM
Modeling the Bolt and Assembly
The bolt, nut, and surrounding components are modeled in 3D. Simplifications such as ignoring threads or using axisymmetric models, can reduce computational cost
Material Properties: The material properties of the bolt (e.g., Young’s modulus, Poisson’s ratio, yield strength) and the clamped parts are defined
Contact Interactions: Contact conditions between the bolt head, nut, and clamped parts are modeled to simulate the interaction and load transfer
Preload Application
Preload Definition: The bolt is preloaded to a specific tension to ensure a secure joint. This preload is applied as an initial condition in the simulation
Preload Methods: Common methods include applying a tensile force, using a thermal expansion analogy, or specifying an initial strain
Analysis Types
Static Analysis: Used to determine the stress and deformation under steady loads
Dynamic Analysis: Used to study the response under time-varying loads, such as impact or vibration
Fatigue Analysis: Used to predict the life of the bolt under cyclic loading

Challenges in Bolt Simulation
Contact Nonlinearity: The contact between the bolt and the clamped parts introduces nonlinearity, making the simulation more complex and computationally intensive
Thread Modeling: Accurately modeling the threads can be challenging due to their complex geometry and the need for a fine mesh
Preload Accuracy: Applying the correct preload and ensuring it is maintained under external loads is critical for accurate simulation results
Contact Interactions
Contact Pairs: Define contact interactions between the bolt head, nut, and the clamped parts. Abaqus provides various contact formulations, such as surface-to-surface contact and node-to-surface contact
Friction: Specify the coefficient of friction between the contacting surfaces to accurately model the frictional forces
Applications
Aerospace: Ensuring the integrity of bolted joints in aircraft structures
Automotive: Analyzing bolted connections in engine components and chassis
Civil Engineering: Evaluating the performance of bolted connections in steel structures
Mechanical Design: Optimizing bolted joints in machinery and equipment
The conclusion from the above statements
Bolt analysis in Abaqus is a comprehensive approach to understanding the behavior of bolted joints under various loading conditions. By accurately modeling the bolt, applying appropriate boundary conditions and loads, and interpreting the results, engineers can ensure the reliability and safety of mechanical assemblies. Despite the challenges, Abaqus provides robust tools and features to perform detailed and accurate bolt analysis, making it an invaluable tool in engineering design and analysis.
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials