Introduction to Metal and Composite Pipes
Pipes are essential in various industries, including oil and gas, water supply, chemical processing, and construction. They are used to transport fluids, gases, and sometimes solids. Two common types of pipes are metal pipes and composite pipes, each with unique properties and applications
Metal Pipes
Metal pipes are made from metallic materials and are widely used due to their strength, durability, and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures. Common metals used include
Carbon Steel
It is the most widely used due to its strength and affordability, Suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, commonly used in oil and gas pipelines, water systems, and structural applications
Stainless Steel
Known for its corrosion resistance and durability, it is Ideal for chemical processing, food and beverage industries, and environments with high moisture or corrosive substances
Copper
Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, often used in plumbing, heating systems, and refrigeration
Aluminum
Lightweight and corrosion-resistant; Used in aerospace, automotive, and some plumbing applications
Ductile Iron
Strong and flexible, resistant to cracking, commonly used in water and wastewater systems
Advantages of Metal Pipes
High strength and durability, It can handle extreme temperatures and pressures, Long service life with proper maintenance, Recyclable and environmentally friendly
Disadvantages of Metal Pipes
Prone to corrosion (except for stainless steel and certain alloys), Heavy and difficult to transport and install, Higher cost for certain metals like stainless steel and copper

Composite Pipes
Composite pipes are made from a combination of materials, typically including polymers, fibers (such as glass or carbon), and resins. These pipes are designed to leverage the strengths of each material while minimizing weaknesses. Common types include
Fiberglass-Reinforced Plastic (FRP)
Made of glass fibers embedded in a polymer matrix, lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and strong, used in chemical processing, water treatment, and offshore oil and gas applications
Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (CFRP)
High strength-to-weight ratio and excellent stiffness, used in high-performance applications like aerospace and automotive industries
Dual-Laminate Pipes
Combine a thermoplastic liner with a fiberglass-reinforced exterior, ideal for highly corrosive environments, such as chemical plants
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) with Reinforcement
Lightweight and flexible, with added strength from reinforcement layers, used in water and gas distribution systems
Advantages of Composite Pipes
Lightweight and easy to transport and install, highly resistant to corrosion and chemical attack, low thermal conductivity, reducing the need for insulation, long lifespan with minimal maintenance
Disadvantages of Composite Pipes
Lower strength compared to metal pipes in high-pressure applications, limited temperature resistance compared to metals, higher initial cost for some advanced composites
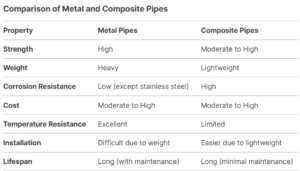
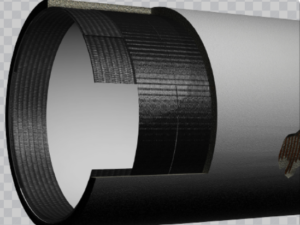
Applications
Metal Pipes: Oil and gas pipelines, water supply systems, structural applications, and high-temperature industrial processes
Composite Pipes: Chemical processing, water treatment, offshore oil and gas, and other applications requiring corrosion resistance and lightweight solutions
The choice between metal and composite pipes depends on the specific requirements of the application, including factors like pressure, temperature, corrosion resistance, and cost. Metal pipes are ideal for high-strength and high-temperature applications, while composite pipes excel in corrosive environments and where weight is a concern. Both types play a critical role in modern infrastructure and industrial processes
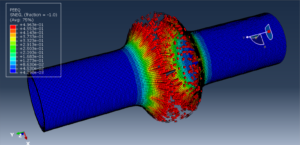
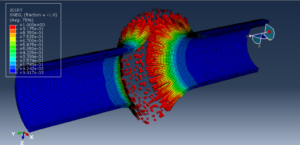
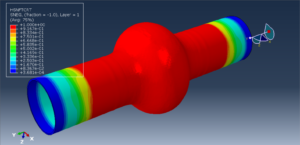
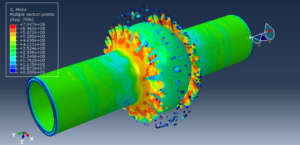
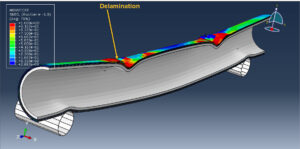
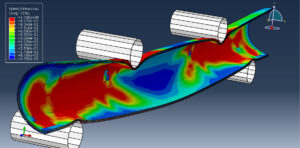
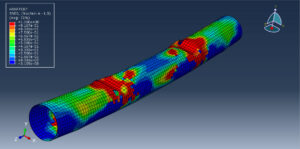
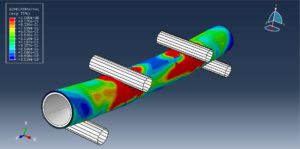
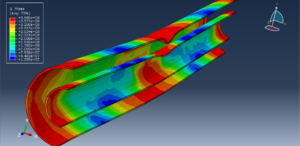
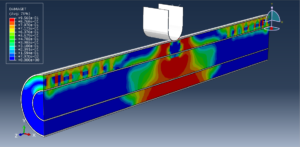
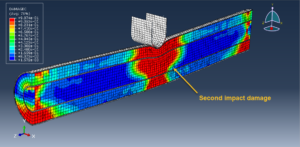
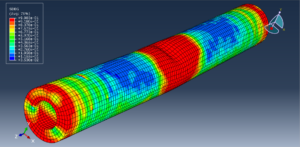
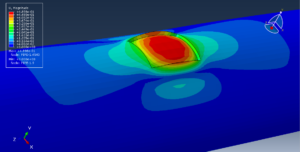
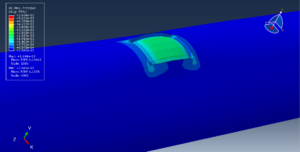
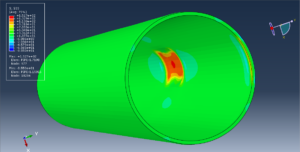
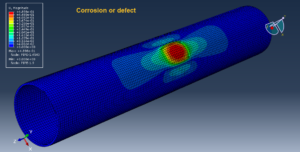
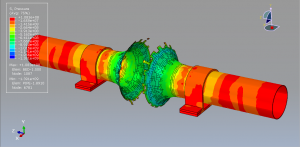
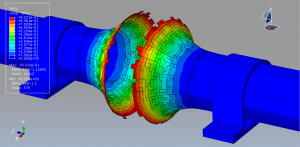
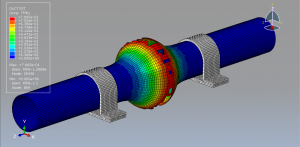
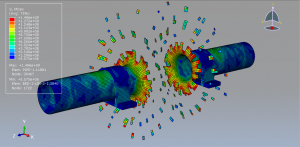
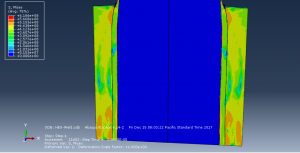
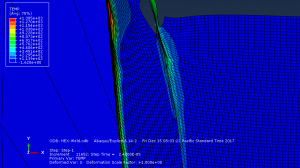
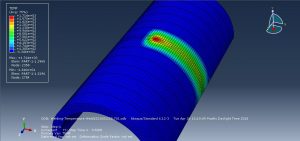
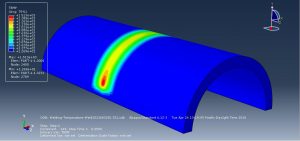
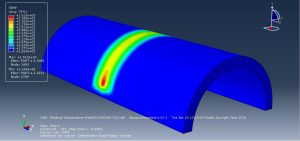
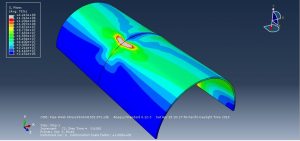
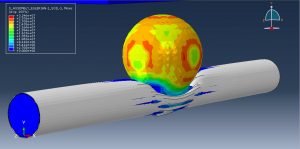
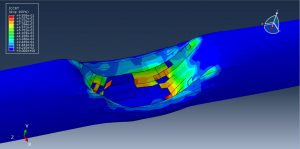
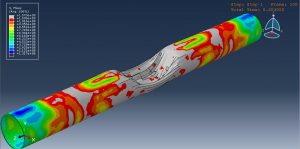
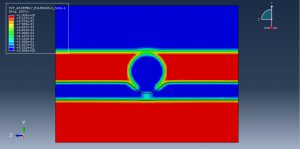
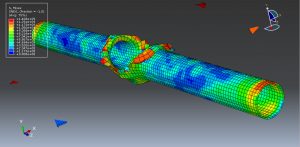
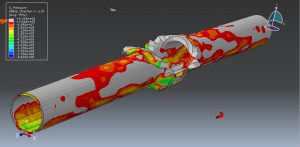
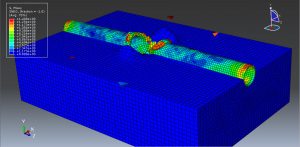
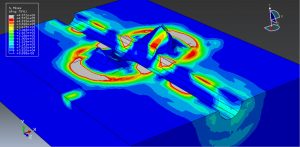
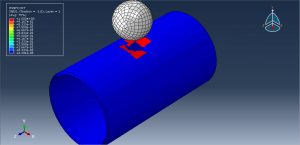
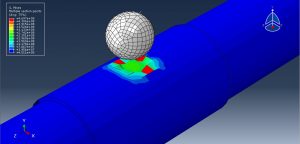
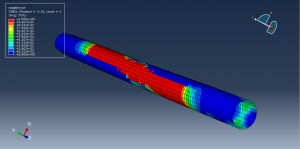
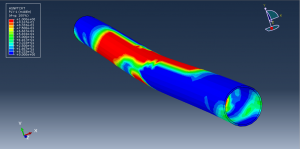
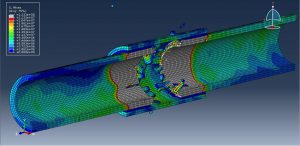
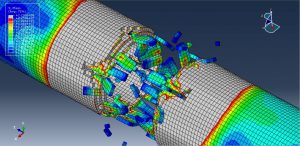
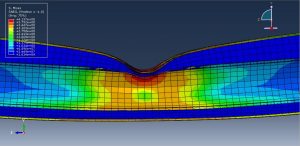
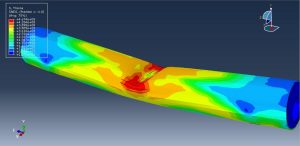
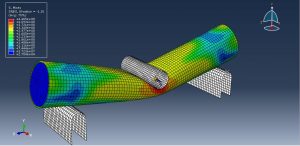
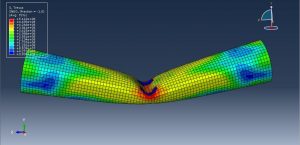
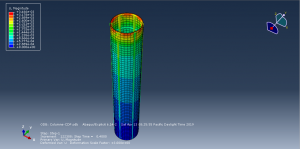
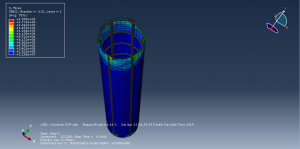
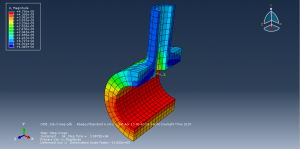
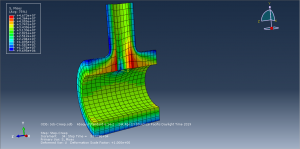
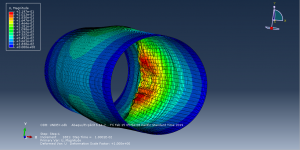
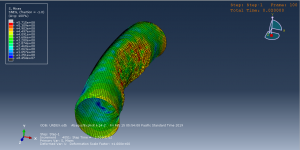
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials