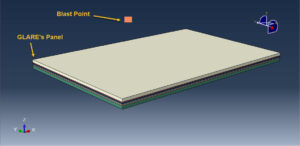
A simulation air blast explosion over a composite GLARE panel in Abaqus has been done in this tutorial. Both aluminum laters are modeled as three-dimensional solid parts. The four glass fiber layers are modeled as three-dimensional solid parts. Because of the symmetry, one-quarter of the whole model is considered. You can see a figure of the assembled parts below
The Johnson-Cook hardening and damage are selected to model aluminum behavior under severe load. Johnson-Cook hardening is a type of isotropic hardening where the static yield stress, is assumed to be of the form. where are the equivalent plastic strain and A, B, n, and m are material parameters measured at or below the transition temperature. The Johnson-Cook criterion is a special ductile damage initiation criterion in which the equivalent plastic strain at the onset of damage is given as an analytical function of the stress triaxiality
The Hashin damage model for the continuum part is considered to model glass fiber. The Hashin criterion identifies four different modes of failure for the composite material. The four modes are tensile fiber failure, compressive fiber failure, tensile matrix failure, and compressive matrix failure
To consider the bone among all surfaces of the aluminum and glass fiber parts, the cohesive interaction method by using stiffness and damage values is selected. The proper boundary conditions and meshes are assigned to the parts
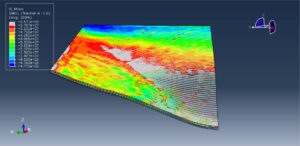
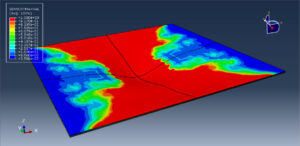
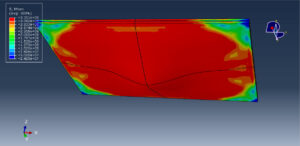
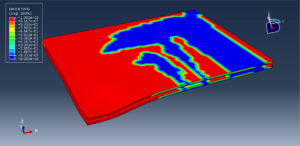
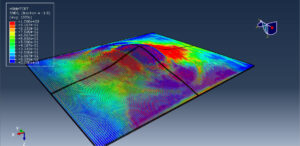
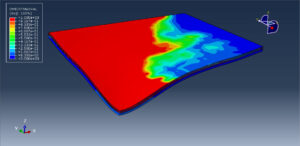
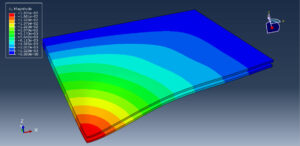
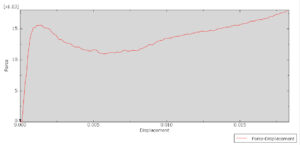
After the simulation, all results such as stress, strain, damage to fiber and matrix, force, and others are available. You can see some figures for the results below
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials