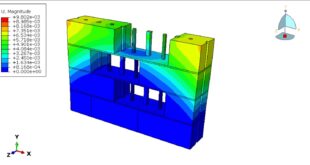
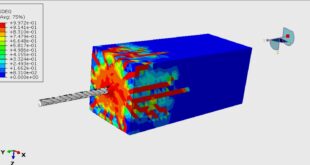
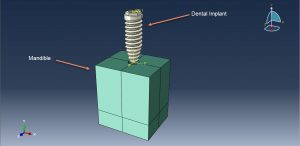
In this tutorial, the simulation dental implant insertion in Abaqus is investigated. Successful osseointegration is a degree of implant stability which occurs after implant integration. This end result is related to two terms, namely primary and secondary implant stability. Primary stability characterizes the mechanical engagement of the implant right after its insertion, while secondary stability is the result of (longer-term) bone regeneration and remodeling (biological process) around the inserted implant. Primary and secondary stability are closely related, as poor primary stability is one of the major causes of implant failure. The finite element method (FEM) is a widely used stress analysis method for the investigation of the biomechanical behavior of bone implant-rehabilitation components, and simulation/evaluation of their mechanical interaction, which is otherwise extremely difficult to investigate experimentally, either in vitro or in vivo. The FEM enables researchers to apply different loadings configurations and determine the displacement and the stress levels experienced by the tooth, prosthesis, implant, and bone. The implanted root is modeled as a three-dimensional part that is imported to the Abaqus because of the complexity. The implant is assumed as a rigid body. The mandible bone is modeled as a three-dimensional solid part. You can see some figures of the model as below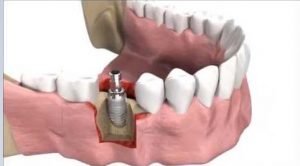
The titanium material is used for the implant root. The mandible bone material is modeled as an elastic material with Johnson-Cook plasticity and Johson-Cook damage with evolution. This material model can predict the damage and failure in the bone during the insertion. The dynamic explicit step with a mass-scale technique is appropriate for this analysis. The interaction is assumed as a general contact which is considered the internal damage by using input file capability. In the interaction section, the rigid body constraint is assigned to the implant part. The fixed boundary condition is used for the mandible part and axial displacement with amplitude and rotational velocity for the implant part is implied. The mesh should be so fine to have a good performance and result
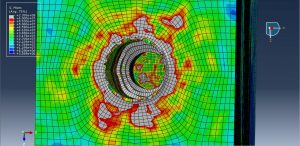
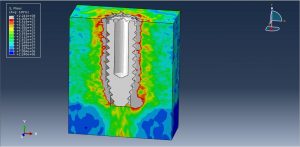
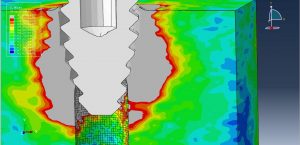
After the simulation all results such as stress, strain, damage, pressure… are achievable. You can see some figures for the results below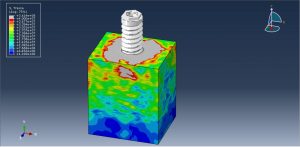
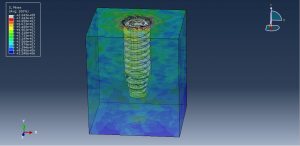
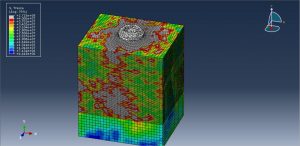
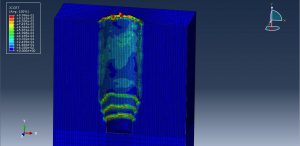
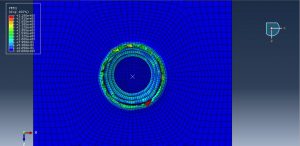
You can provide CAE ,INP,and English video files of this simulation here. The cost of these files is Thirty Euros. you can click on the bellow bottom to beginning process
You can purchase the tutorial through a PayPal account, a Visa, or a Master card, just before payment,send me an email to this address: karampourp@gmail.com
 Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials
Abaqus tutorials Abaqus tutorials